Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) has significantly advanced the world of 3D printing, enabling the creation of complex and durable parts by fusing powdered materials with a laser. However, the process is not without its drawbacks. One significant challenge is the limited reusability of the powder. After a few print cycles, the powder quality diminishes, rendering it unsuitable for further use in the SLS printer. This often leads to substantial waste as leftover powder is discarded. Fortunately, there is a sustainable solution: reprocessing this powder using the Filabot system to create filament for FDM (Fused Deposition Modeling) 3D printers or pellet printers. This approach not only reduces waste but also maximizes material efficiency and promotes environmental responsibility.
The Problem with SLS Powder Waste
In the SLS printing process, a laser selectively fuses layers of powder to build the desired object. While this technique is highly effective, not all of the powder is consumed in the parts being printed. A significant portion of the powder remains unused, and after several cycles, it loses its quality due to thermal degradation and contamination. Traditionally, this leftover powder is considered waste and is often disposed of, leading to increased costs and environmental impact.
Filabot: The Sustainable Solution
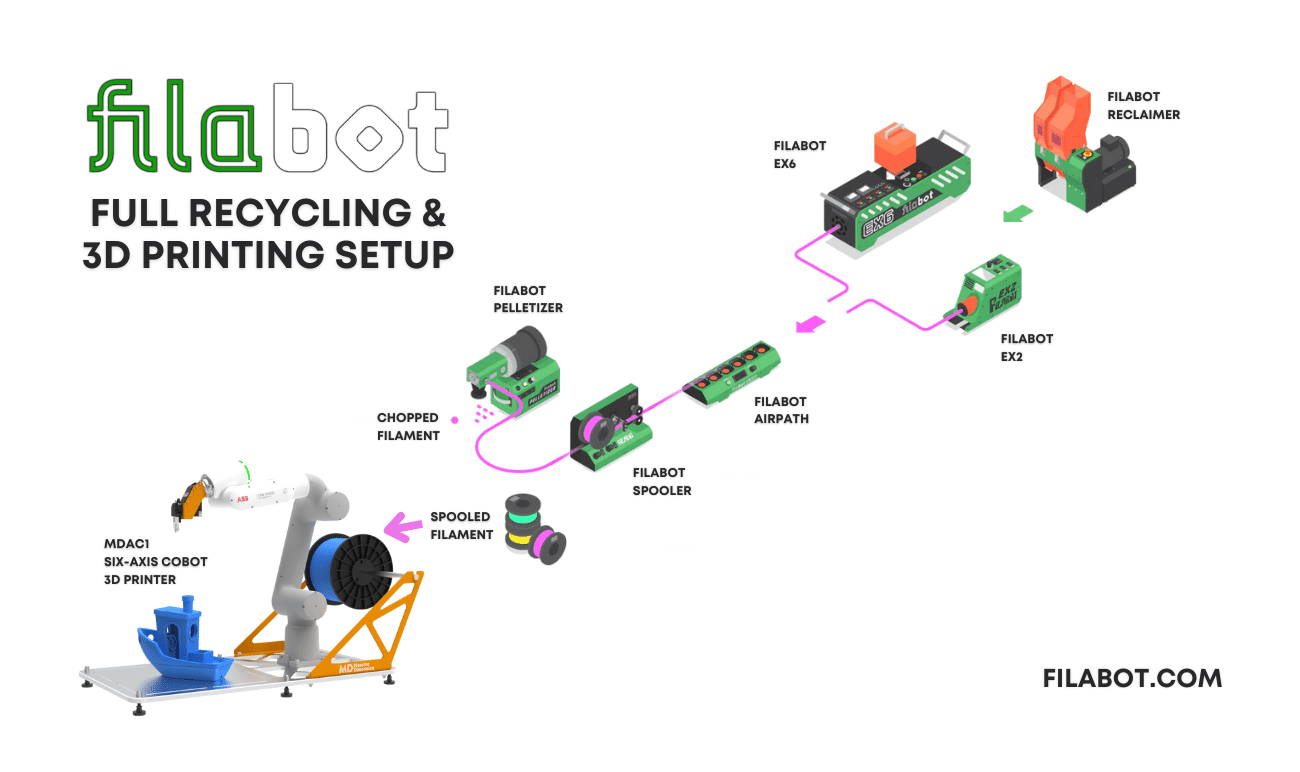
Filabot, a versatile and innovative system can be used to reprocess various plastic materials into filament for FDM 3D printers or pelletized for pellet printers. With Filabot, the leftover SLS powder, which would otherwise be discarded, can be transformed into high-quality filament. This not only gives the material a new lease on life but also significantly reduces the environmental footprint of the SLS printing process. Secondly SLS printed parts can also be ground up and also extruded into new filament for FDM printing.
Materials Used in SLS Plastic Printing
SLS printing primarily uses a variety of plastic powders, each with distinct properties that make them suitable for different applications. The most common materials used in SLS printing that can be converted with the Filabot system include:
- Nylon (PA 12 and PA 11): Nylon is widely used in SLS printing due to its excellent mechanical properties, durability, and flexibility. Both PA 12 and PA 11 powders can be reprocessed into filament for FDM printers, allowing for high-strength, functional prototypes and end-use parts.
- Polypropylene (PP): PP is valued for its chemical resistance, elasticity, and toughness. Reprocessing PP powder into filament enables the creation of durable and versatile parts using FDM printers.
- Thermoplastic Polyurethane (TPU): TPU is known for its elasticity and resilience, making it ideal for parts that require flexibility and impact resistance. Reprocessing TPU powder into filament enables the creation of flexible, durable parts using FDM printers.
Reprocessing SLS Powder into Filament
The process of reprocessing SLS powder using the Filabot system is straightforward yet highly effective:
- Collection and Preparation: Collect the leftover SLS powder from the printer. Ensure that the powder is clean and free from contaminants.
- Material Drying: Remove moisture from the used powder and ground up parts.
- Melting and Extrusion: The collected powder is fed into the Filabot extruder, where it is melted and extruded into a continuous filament. Filabot's advanced extrusion technology ensures consistent filament quality, suitable for use in FDM 3D printers.
- Spooling and Storage: The extruded filament is then spooled and stored, ready for future use. This filament can be used in any FDM 3D printer, enabling the production of new parts without the need for new material.
Reclaiming SLS Printed Objects
In addition to reprocessing leftover powder, the Filabot system can also reclaim SLS printed objects. Often, SLS prints may need rework or may be prototypes that are no longer needed. Instead of discarding these objects, they can be ground down and fed into the Filabot system to create new filament. This further enhances the sustainability of the SLS process by ensuring that every bit of material is utilized to its fullest potential.
Benefits of Using Filabot for SLS Reprocessing
- Cost Savings: By reprocessing leftover powder and printed objects, businesses can significantly reduce the cost of raw materials.
- Waste Reduction: Transforming waste powder and objects into usable filament minimizes the amount of material that ends up in landfills.
- Enhanced Sustainability: Utilizing the Filabot system promotes a circular economy, where materials are continuously reused, reducing the environmental impact of 3D printing.
- Versatility: The Filabot system is compatible with a wide range of thermoplastics, making it a valuable addition to any 3D printing operation.
Conclusion
The Filabot system offers a powerful solution to one of the key challenges of SLS 3D printing: waste management. By reprocessing leftover powder and reclaiming printed objects into filament, Filabot not only maximizes material efficiency but also contributes to a more sustainable and cost-effective 3D printing ecosystem. Embracing this technology allows businesses to reduce their environmental footprint, lower material costs, and promote a more responsible approach to additive manufacturing. With Filabot, the future of 3D printing is not only innovative but also sustainable.